The Making of SciePro’s Male and Female 3D Human Anatomy Models
Why 3D Anatomy Accuracy Matters
If you’re developing a medical app, surgical simulator, or VR/AR training platform, the quality of your 3D human anatomy model determines the credibility of your product. Many assets look polished at first glance but fail under real scrutiny — mesh intersections, missing structures, and anatomical mistakes are common. That’s why we spent over ten years building complete male and female 3D anatomy models that meet the highest standards of accuracy, performance, and reliability.

A Decade of Research and Development
The project started with a skeleton, but quickly grew into a full human body: bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, cardiovascular, lymphatic, and nervous systems. From the beginning we aligned our work with the Terminologia Anatomica (TA), the international standard for anatomical nomenclature. The TA was our baseline — every structure we created was checked against it. But we didn’t stop there. Over the years we added many structures that go beyond the TA, and our long-term goal is to also include the remaining entries from the Terminologia Neuroanatomica (TNA) to cover the brain and nervous system in even greater detail.
At the start we experimented with MRI and CT datasets. They helped with orientation but were far from sufficient: too low in resolution, inconsistent across individuals, and often distorted by pathology. We realized quickly that for a clean, reliable baseline model, we needed broader and higher-quality sources. That meant cadaver material, classical anatomy references, macro photography, and continuous expert input.

Learning Anatomy First-Hand
Some parts of the body are extremely hard to understand from books alone. To overcome this, we took our 3D artists into cadaver labs, so they could study the structures directly. Seeing and handling real anatomy helped the team model with more confidence and precision.
We also conducted an extensive photographic session at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE). Those reference images became invaluable later when we entered the texturing stage, especially for the realistic look of tissues and surfaces.

Coordinating a Team of Experts
At peak times, up to 15 people were working on the models simultaneously. That scale brought its own challenges: making sure every tendon attaches to the right bone, every vessel follows its correct course, and no system overlaps incorrectly with another. Coordination was critical. We built strict versioning and review workflows, so that when all the pieces came together, the body fit seamlessly as a whole.
Every structure was reviewed by multiple specialists, compared against literature, and adjusted until expert consensus was reached. It was an iterative process, often taking weeks or months for a single subsystem. But it was the only way to guarantee consistency and accuracy at scale.
Applications Beyond Education
- Hospitals: Patient communication tools
- Pharma & MedTech: Product demonstrations
- Research: Advanced anatomical analysis
- Creative industries: Film, gaming, and AR/VR
Building Medically Accurate 3D Models
Accuracy in anatomy modeling isn’t only about the right shapes. It’s about building models that survive production pipelines without breaking. That’s why we enforce a strict no mesh intersections rule. Thousands of structures interlock inside the body, but in 3D space they must fit precisely to avoid rendering or printing errors.
Topology matters too. Our models are 99.9% quads, cleanly retopologized and organized into logical hierarchies. That makes them suitable for anything from high-resolution rendering in 3ds Max or Blender to real-time visualization in Unity and Unreal Engine.
Textures are created at 8K resolution for maximum fidelity, but we also provide optimized sets for WebGL and mobile use. This ensures the same model can power a cinematic animation, an interactive training app, and even a 3D print.
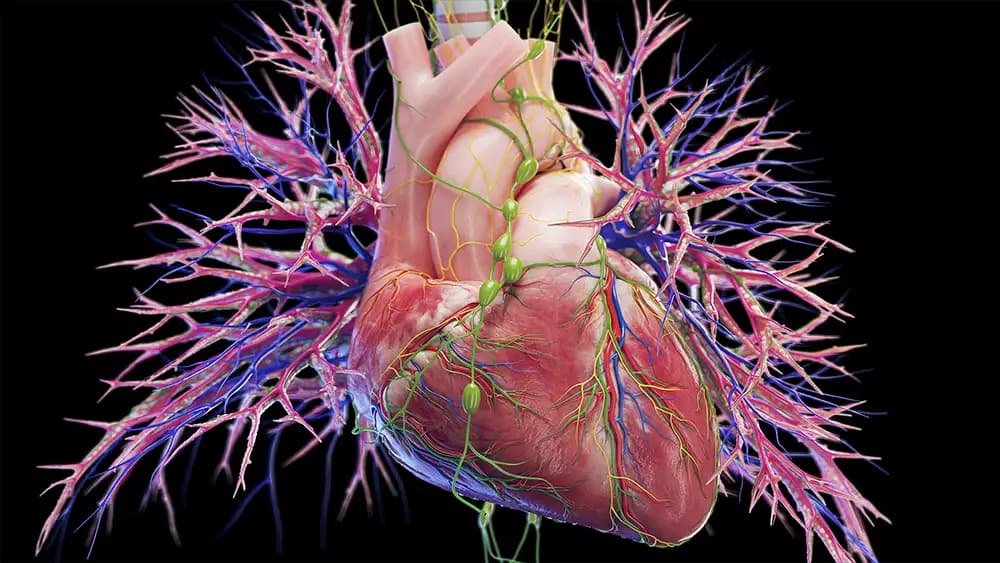
Thousands of Hours on the Heart
The heart was one of the toughest structures. We spent thousands of hours modeling valves, papillary muscles, and coronary vessels down to the finest detail. The original rig was highly complex to allow physiologically realistic motion. Simplified versions were later created for WebGL and iOS tests, but the core model remains one of the most detailed 3D hearts available.
You can read more in our dedicated Heart Making Of article, where we explain how we translated raw data and medical expertise into a production-ready heart.

Male and Female 3D Anatomy Models
From day one we committed to building both male and female anatomy models. This was about more than completeness. In education and healthcare, inclusivity matters. Students, professionals, and developers need accurate male and female references across all systems. Our models maintain consistency across both sexes, so switching between them doesn’t introduce gaps or contradictions.

Why Clients Choose SciePro’s Anatomy Models
Clients tell us the difference is obvious. Our models are medically accurate, because they’re reviewed by experts and aligned with international standards. They are production-ready, thanks to clean topology and no intersections. They integrate smoothly into Unity and Unreal, where performance matters. And they come with clear licensing and IP security, so projects never run into legal risks.
For developers, this means faster integration and fewer technical issues. For educators and healthcare companies, it means accuracy that can be trusted by professionals.
Advanced Insights
What About Accuracy?
SciePro’s Complete Human Anatomy Model took over 115,000 man-hours to create. Every detail was cross-checked by surgeons and medical illustrators.
Textures & Platforms
- 8K+ textures for maximum realism
- Compatible with 3ds Max, Blender, Maya, Unity, Unreal
Comparing Learning Tools
| Feature | Cadaver Labs | Textbooks | 3D Anatomy Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Limited | High | High |
| Interactivity | Low | Low | Very High |
| Cost Efficiency | High | Medium | Scalable |
| Digital Integration | None | None | Full (VR/AR) |
The Work Continues
Even after more than ten years, the work isn’t done. We are expanding into pathologies, anatomical variants, and subsystem packs, while continuing to add structures from the TNA. Each update follows the same principles: accuracy, medical validation, and production reliability.
FAQ
Are 3D anatomy models replacing cadaver studies?